Equipment
Pulsed Laser Deposition
Located in Kemper 120
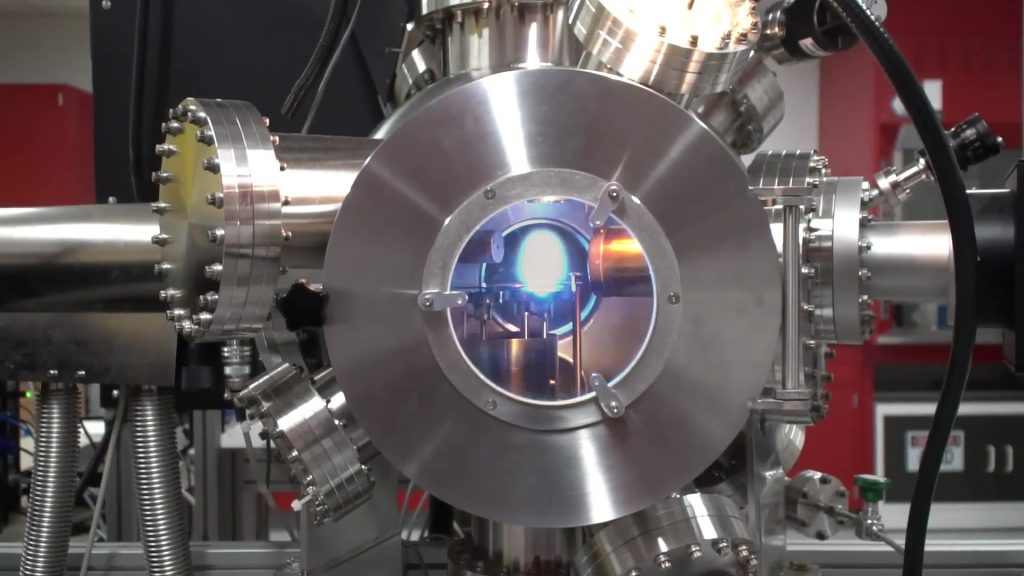
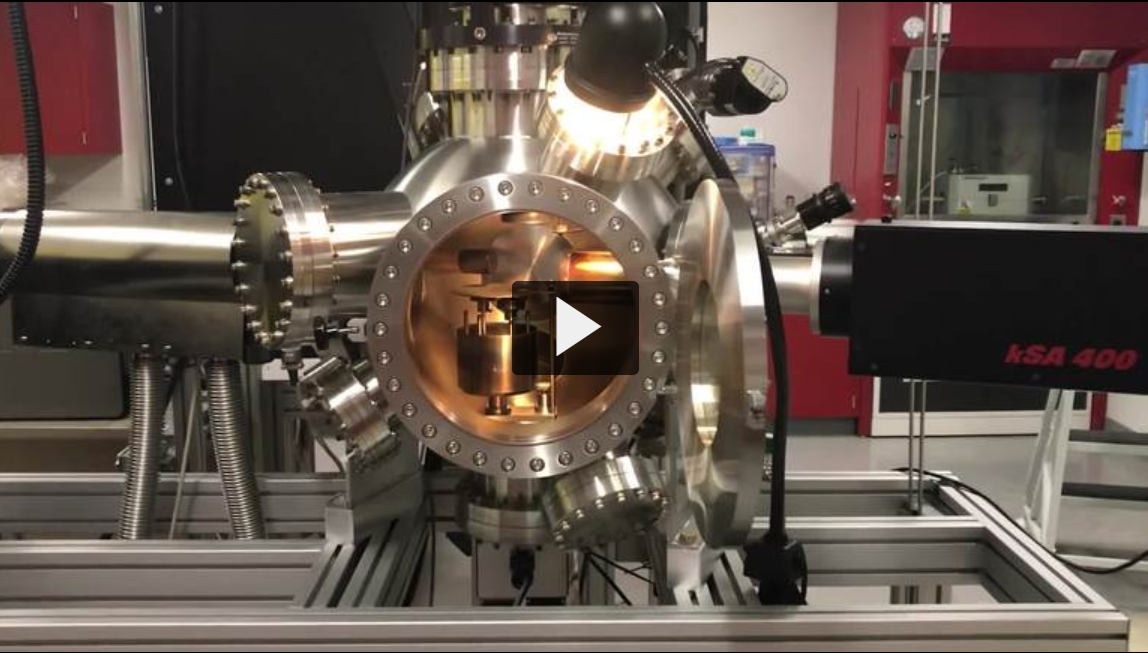
Pulsed laser deposition (PLD) refers to a thin film growth technique that uses a pulsed laser to ablate material from a ceramic target which then deposits on a substrate. This technique permits the growth of high quality thin films and superlattices of perovskite structured materials with atomic layer precision. A reflective high energy electron diffraction (RHEED) system provides in-situ monitoring of the growth process, including determination of the growth mechanism (layer-by-layer, step flow or three dimensional island growth) and counting of the growth of individual atomic layers. We have installed a state-of-the-art PLD system from NBM Design equipped with a KrF (248 nm) Coherent Compex Pro 201 laser. The system is capable of growing films of up to six different materials while varying the deposition conditions over a wide range of substrate temperatures (RT to 1100 °C), oxygen/nitrogen pressures (10-7 to 1 torr) and with adjustability of the x-y-z position of the substrate heater.
Videos of the PLD system (links to Aggie Video)
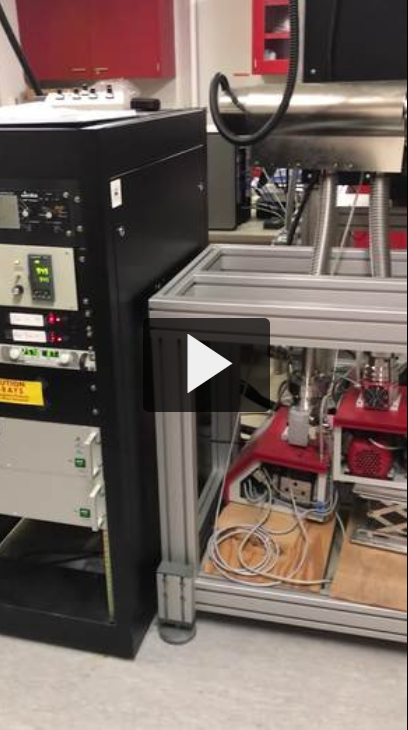


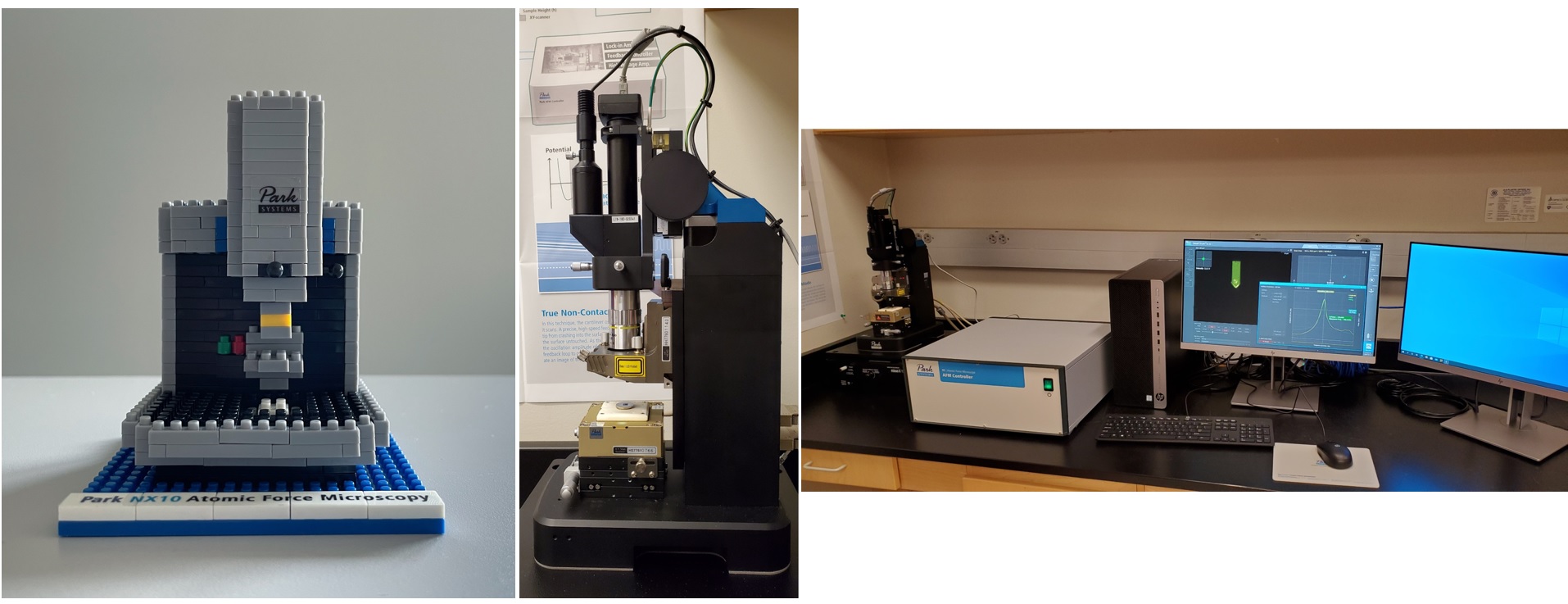
Lego PLD system: Created by Michael Lee
 |  |
Thin Film X-Ray Diffraction
Located in the Advanced Materials Characterization and Testing (AMCaT) Laboratory – Kemper 135
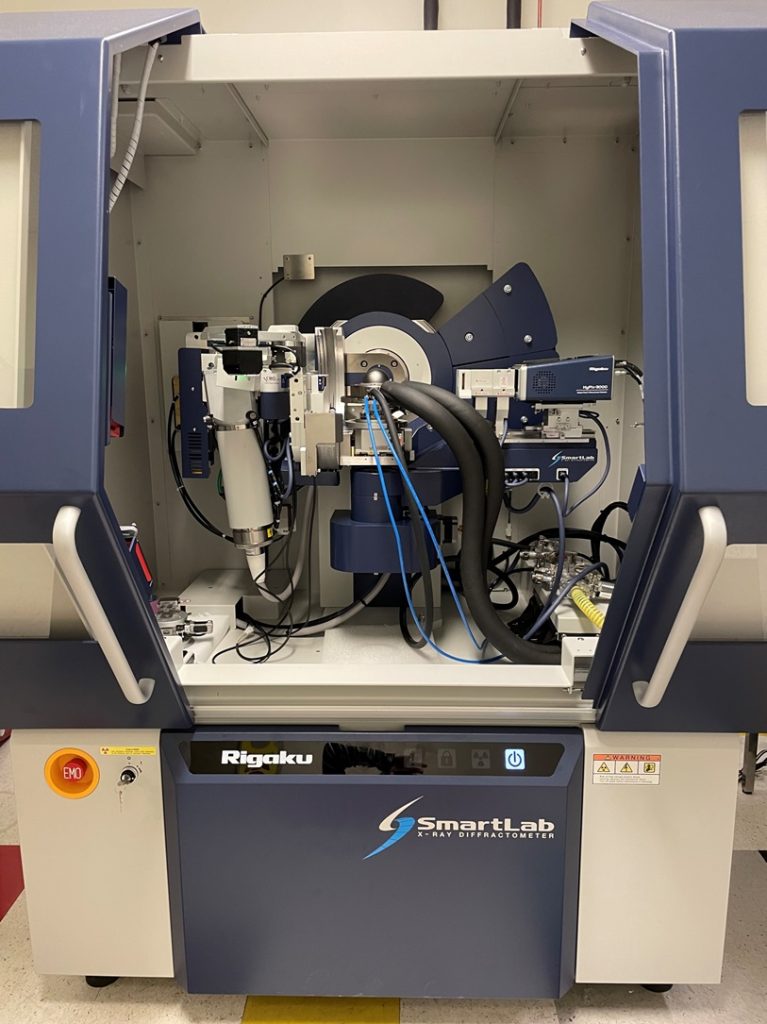

Rigaku SmartLab Thin Film X-ray Diffraction System (acquired via MRI award #2216198, PI: Yayoi Takamura, co-PIs: Kukreja, Hong, Velazquez, Sen) is dedicated for the full structural characterization of thin film samples. These capabilities will include x-ray reflectivity, high-resolution x-ray diffraction, reciprocal space maps (RSMs), pole figures, texture analysis, and grazing incidence x-ray diffraction. The system will be equipped with a state-of-the-art 2D HyPix-3000 detector to enable high-resolution measurements in 0D, 1D, and 2D modes leading to substantial decreases in data acquisition times (i.e., RSM measurements which would take 6+ hours on the predecessor Bruker D8 Discover and PANalytical X-Pert Pro diffractometers, can be acquired within a few minutes). In addition, it features dual energy discriminators which allows the user to adjust the energy threshold to suppress fluorescence and to eliminate cosmic rays and white radiation for optimized signal-to-noise. The Cross Beam Optics (CBO) with parabolic mirror allows for both parafocusing Bragg-Brentano geometry as well as parallel beam geometry in combination with a Ge (220) 2-bounce incident beam monochromator to select only Cu Kα1 radiation. The rapid acquisition times will enable in situ measurements as a function of temperature using low/high temperature and environment-controlled sample stages (Anton Parr DSC 500 – capable of reaching temperatures from -180 °C to 500 °C). The in-plane diffraction attachment provides and additional detector scanning axis orthogonal to the theta/2-theta diffraction plane allowing measurement of planes parallel to the sample surface. This degree of freedom greatly improves the diffractometer versatility and allows the measurement of in-plane structure factors from epitaxial films, in-plane reciprocal space maps from ultra-thin (a few nm) films, and full pole figures without the need for sample re-mounting and transmission measurements as required by conventional Eulerian cradle geometries. A MicroArea Measurement package consists of a CBO-f polycapillary which converts the line focus parallel beam from the CBO parabolic mirror into a point shaped beam of 400 microns in diameter. It enables high intensity point focus applications without switching the x-ray tube from line to point focus position. A CCD camera is available for sample positioning and viewing. Furthermore, the enclosure is large enough to support ancillary equipment for the application of electric fields and laser illumination.
Lego XRD system – Created by Tom Wynn
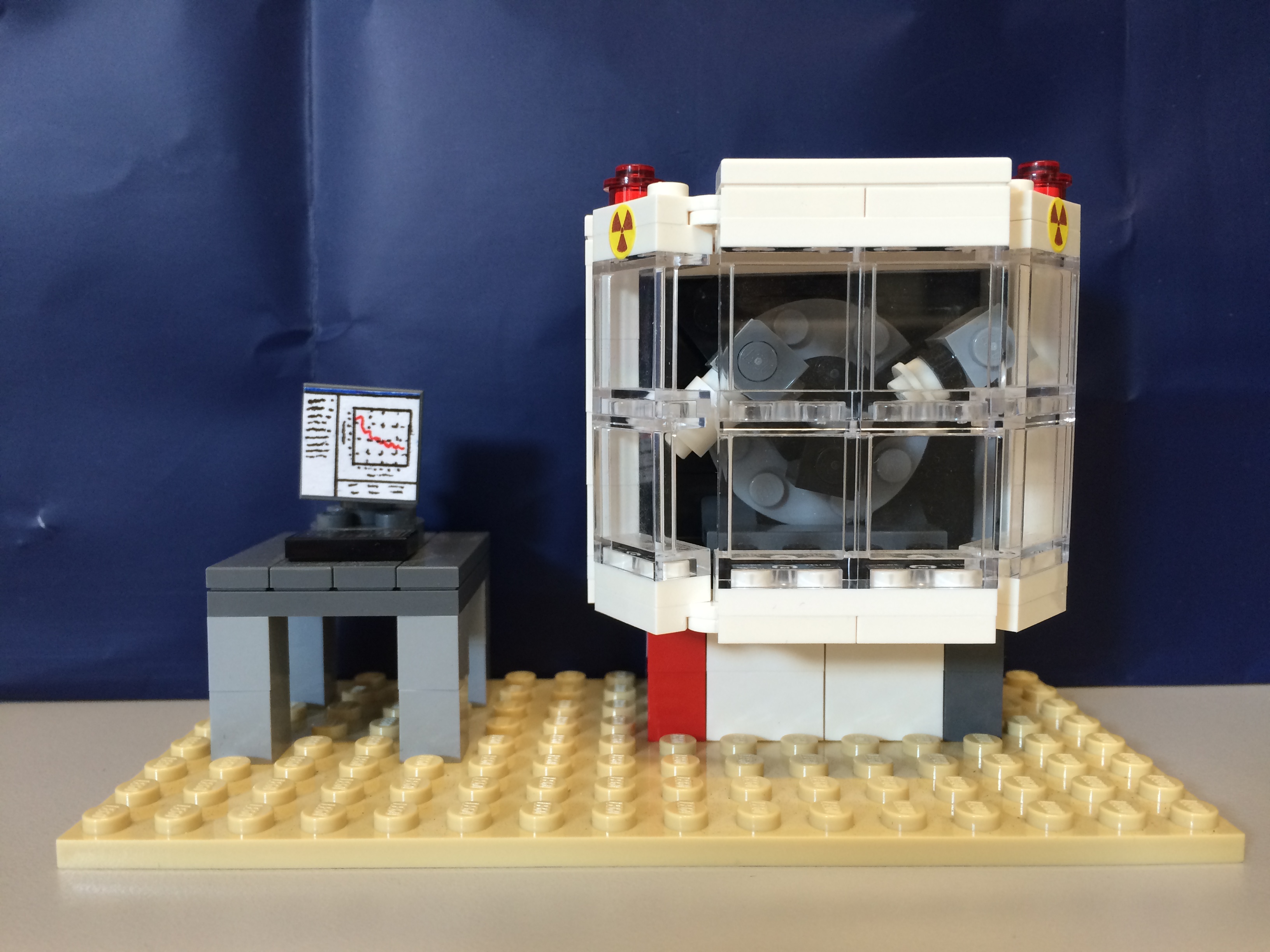

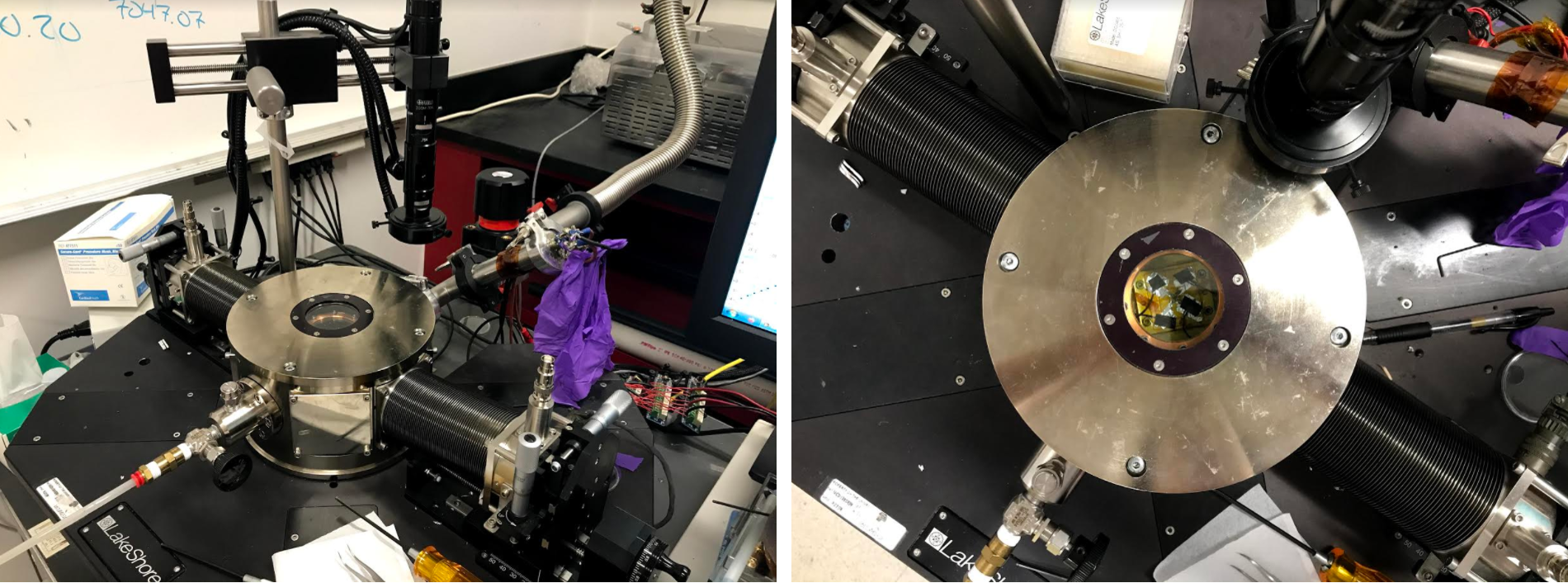
Cryogenic Probe Station
Located in Kemper 116/169
The Lakeshore Cryotronics TTPX cryogenic probe station is used for the electrical characterization of thin film samples. The system is capable of measuring I-V curves as a function of temperature ranging from 4.2 to 475 K and is currently equipped with two micro-manipulated probes.
Shared Equipment
Park Systems XE7 Scanning Probe Microscopy – shared with the Hong and Kukreja groups
Located in Ghausi 1111
The Park Systems XE7 Scanning Probe Microscope is used to obtain high resolution images of the surface topography of samples. Advanced modes include magnetic force microscopy, conductive tip atomic force microscopy, and piezoforce microscopy.
Beamlines at the Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Photoemission Electron Microscopy (PEEM) – BL11.0.1.1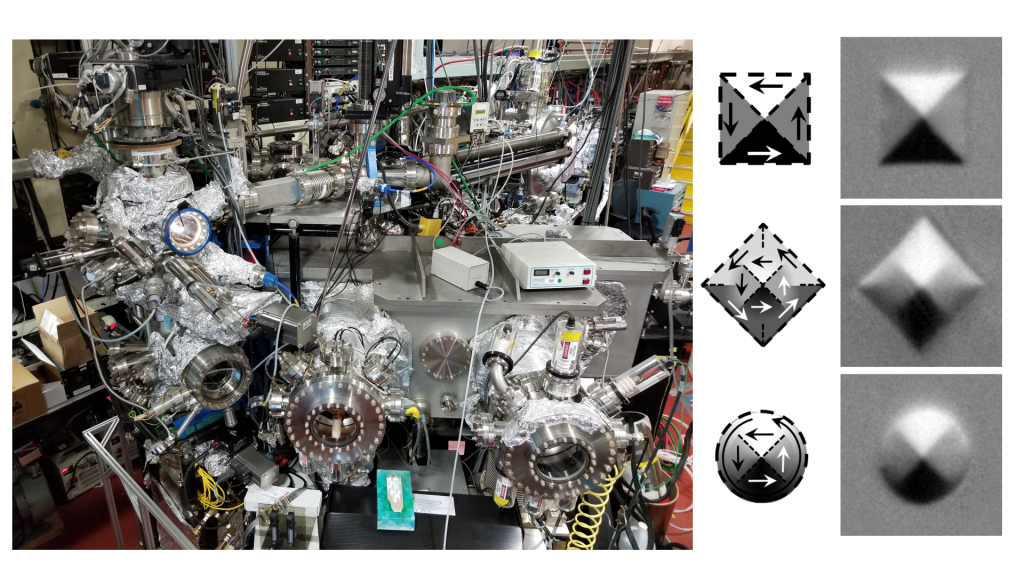
Soft X-ray Magnetic Spectroscopy – BL4.0.2
Soft X-ray Magnetic Spectroscopy – BL6.3.1

Beamlines at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Resonant X-ray Reflectometry – BL2-1
High Resolution X-ray Diffraction – BL17-2
Commonly Used Software
Leptos from Bruker AXS – Fitting of X-ray Reflectivity and X-ray Diffraction Data | 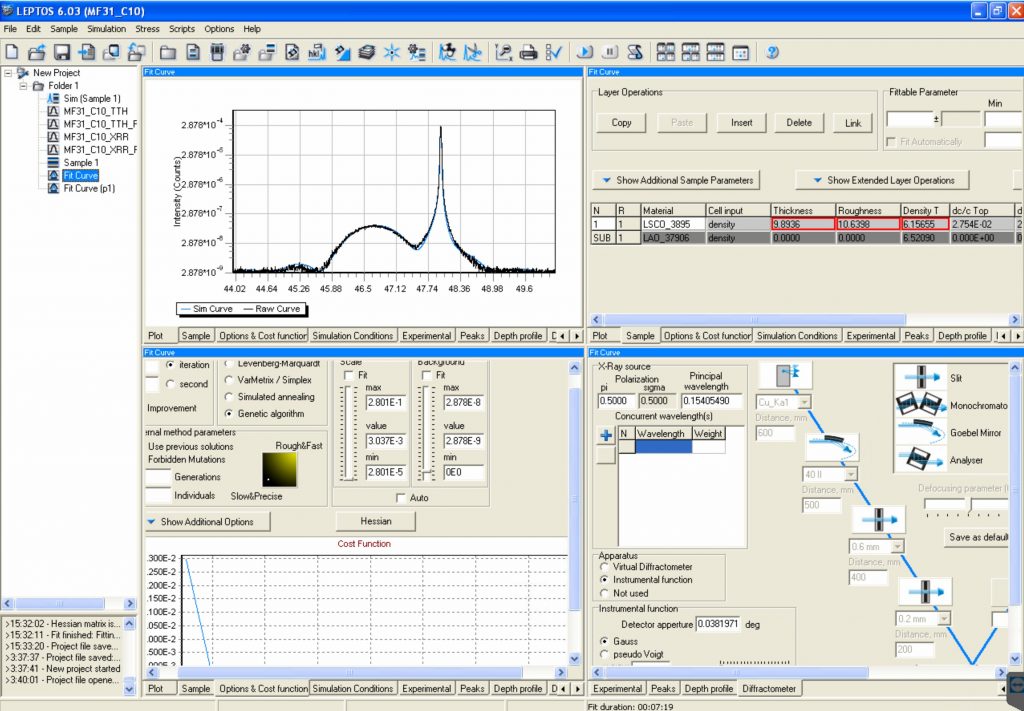 |
GenX – Fitting of (Resonant) X-ray Reflectivity and Polarized Neutron Reflectometry DataAvailable for download here. Oak Ridge National Laboratory has tutorials here. | 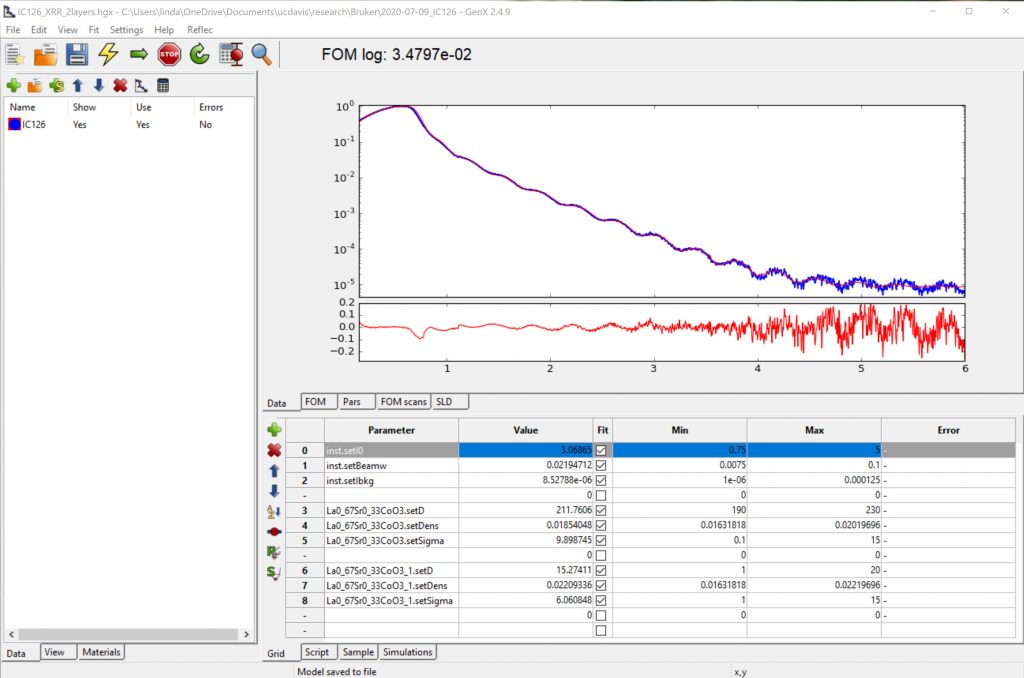 |
ReMagX – Fitting of Soft X-ray Magnetic Reflectivity DataMore information available here. | 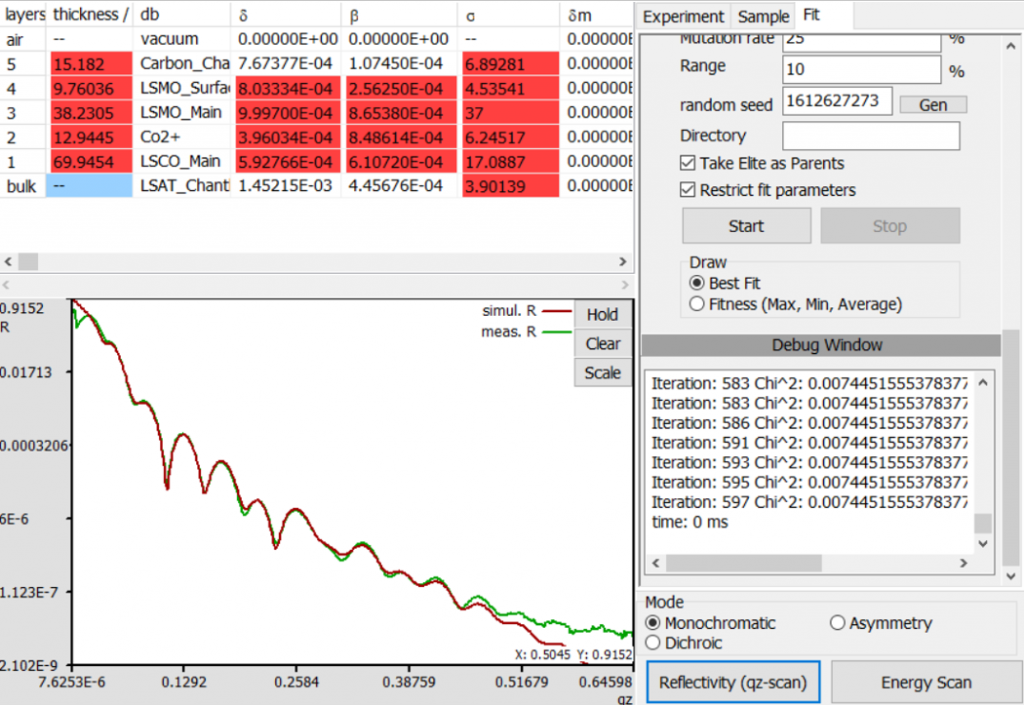 |
MuMax3 – Micromagnetic Simulations of Patterned NanostructuresAvailable for download here. | 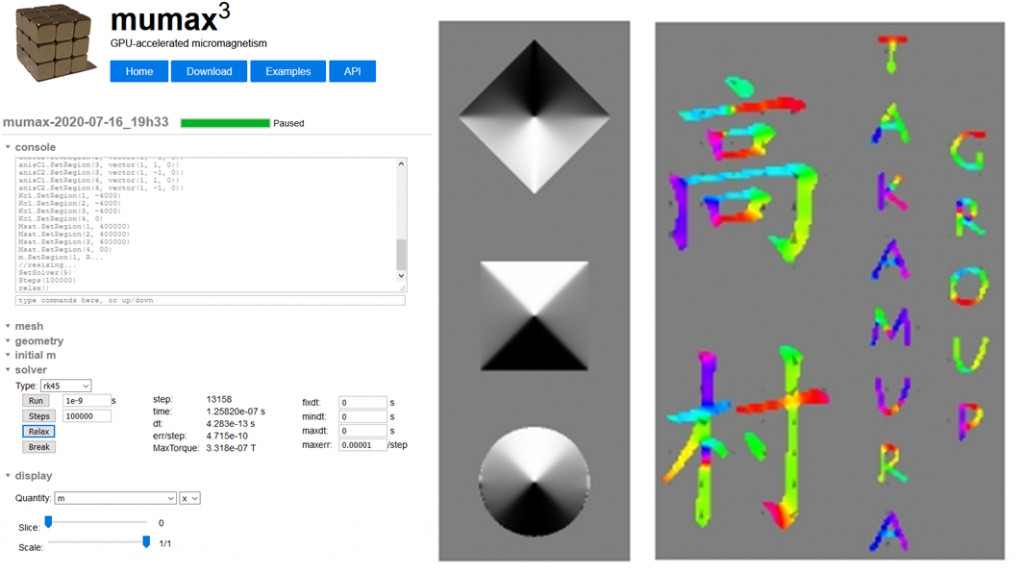 |
